-
Mobile Version
Scan with Mobile
- Member Center

Extraction section
Production Line Introduction: This production line is a modern production line that integrates efficiency, intelligence, and sustainable development. We focus on producing a variety of types and distinctive products, ensuring the precision and efficiency of each process through carefully designed production processes and cutting-edge core technologies. The production line has achieved high automation and intelligence, not only improving production efficiency, but also ensuring strict control of product quality. At the same time, we focus on environmental protection and sustainable development, striving to achieve optimal resource allocation and minimal environmental impact in the production process.
Natural phospholipids
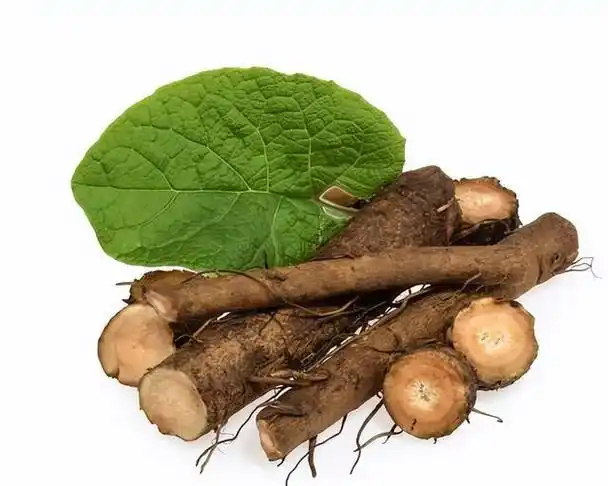
Herbal extract
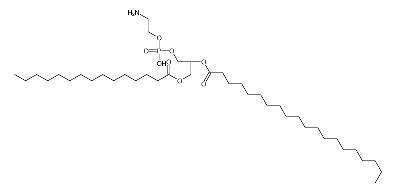
PE
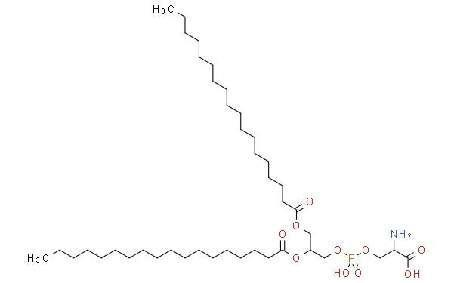
PS(提取非合成)
PS(提取非合成)
Siraitin
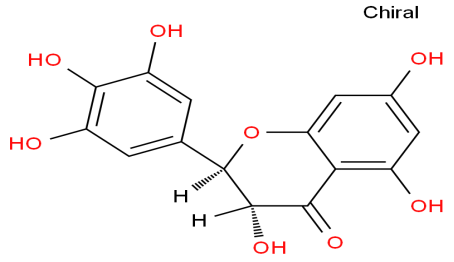
Dihydromyricetin
Dihydromyricetin
Root bark glycoside
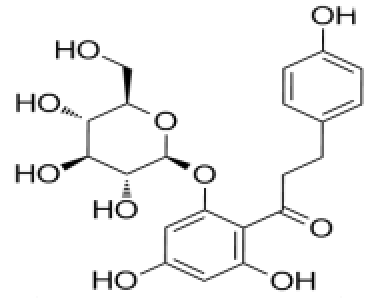
chlorogenic acid
chlorogenic acid